Signs & Symptoms of Vitamin C Deficiency

Signs & Symptoms of Vitamin C Deficiency
Posted on 12th Feb, 2023
Vitamin C or Ascorbic acid, is an essential nutrient required by our body in order to ensure optimum health and function. A deficiency in vitamin C, leads to a reversible but fatal if untreated condition called ‘Scurvy.’ In this article, let us take a closer look at the signs and symptoms of a Vitamin C deficiency.
What is Scurvy
Collagen is an important component in the production of healthy connective tissue. A lack of Vitamin C inhibits the bodies ability to produce collagen, thus leading to a host of symptoms. Fortunately, supplementation of vitamin C either through food or synthetic sources will result in a speedy and full recovery, although left untreated, can cause death.
Symptoms of a Vitamin C deficiency
Dry and damaged skin:
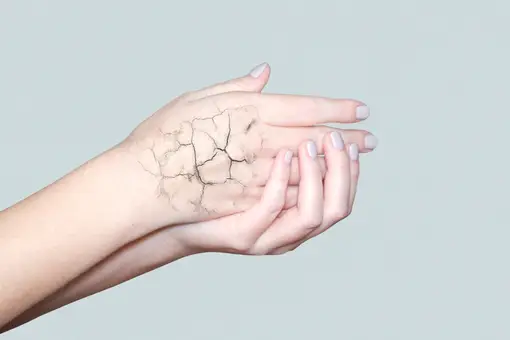
In healthy skin, the epidermis is filled with Vitamin C, and collagen production is at its optimum level. Thus, when skin starts to appear dry and lifeless, it could indicate a low level of vitamin C, due to inhibition of collagen production, which is essential for healthy skin.
Slow wound healing:

Once again, collagen is an essential component of the body’s ability to heal wounds. Low levels of vitamin C, thus have a direct impact on collagen levels which in turn negatively impact the wound healing process. This however, is a symptom only encountered in advanced stages of scurvy.
Gingivitis:
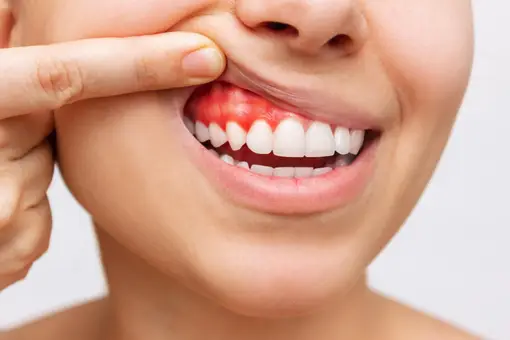
Deficiency of Vitamin C can lead to gingivitis, which is a condition that affects the gums, causing them to swell and bleed. In case of prolonged and advanced deficiency, a purple discoloration may develop and the person may also start to lose their teeth.
Joint Pain:
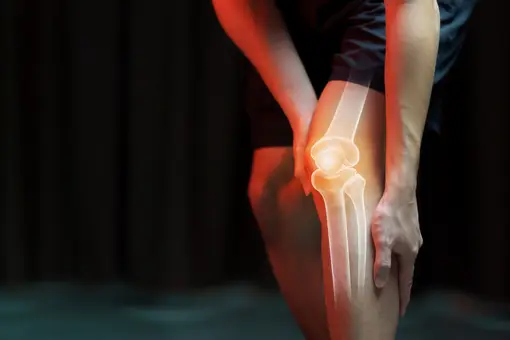
Joints are composed of cartilage that is primarily made of collagen and thus low levels of vitamin C results in decreased padding around the bone areas which ultimately leads to joint pain. Swelling and inflammation around the bones and joints is also common.
Decreased Immunity:

Vitamin C is an integral requirement for immune cells and the immune system as a whole to function holistically and optimally, thus protecting the body against foreign invaders such as bacteria and viruses. Thus, it stands to reason that, a vitamin C deficiency results in decreased immunity and a higher risk of infection, also including serious illnesses like pneumonia.
Fatigue and Mood Disorders:

A low level of vitamin C leads to fatigue and other mood disorders. These may be the initial symptoms and tend to clear up fairly quickly after adequate vitamin C supplementation.
Dosage
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) of vitamin C varies depending on age and gender. Here are the RDAs for vitamin C:
- Infants (0-6 months): 40 mg
- Infants (7-12 months): 50 mg
- Children (1-3 years): 15 mg
- Children (4-8 years): 25 mg
- Children (9-13 years): 45 mg
- Teens (14-18 years): 65-75 mg
- Adults (19 years and older): 75-90 mg for women, 90 mg for men
- Pregnant women: 85 mg
- Breastfeeding women: 120 mg
However, some experts suggest higher doses of vitamin C, up to 1000 mg per day, may provide additional benefits for certain health conditions. It's always best to consult with a healthcare professional before taking high doses of any supplement.
Side Effects and Warnings
Vitamin C is generally considered safe when consumed in recommended amounts. However, taking high doses of vitamin C supplements can cause some side effects such as:
- Digestive issues: Large doses of vitamin C may cause gastrointestinal issues like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps.
- Kidney stones: High doses of vitamin C can increase the risk of developing kidney stones, particularly in people with a history of kidney stones.
- Iron overload: Vitamin C can enhance the absorption of iron from food, which can be harmful to people with hemochromatosis, a condition that causes iron overload in the body.
- Interference with medical tests: High doses of vitamin C can interfere with certain medical tests, such as blood glucose tests and stool tests.
It's important to stick to the recommended daily dosage of vitamin C and to consult with a healthcare professional before taking high doses of vitamin C supplements.

Health articles from our experts
Finding Out the Best Daily Wellness Supplements

15 Iron-Rich Foods in India to Increase Hemoglobin

Top 8 Fruits Rich In Vitamin B 12

10 Best Vitamin B Foods For Vegetarians

10 Best Indian Foods Rich In Folic Acid
Signs & Symptoms Of Omega 3 Deficiency

7 Ways to Prevent Vitamin A Deficiency

Signs & Symptoms of Vitamin C Deficiency

6 Fruits rich in Vitamin B

