Understanding BMI: The Key to Weight-Health Connection
Understanding BMI: The Key to Weight-Health Connection
Posted on 16th May, 2024
Whether you're an athlete, a gym enthusiast, a corporate employee, or a homemaker, at some point in your life, you've likely wondered if your weight is proportionate to your height.
This is precisely where BMI (Body Mass Index) comes into play. It's a widely discussed metric when it comes to fitness and health.
You too can calculate your BMI using the calculator below and find out where you stand.
BMI CALCULATOR
BMI (Body Mass Index) indicates whether a person has a healthy weight for their height. Enter your height and weight to calculate your BMI.
Now that you know your BMI, let's dive deeper into how it works, how to interpret it, whether it's truly worth knowing, what you can do with this information, and much more.
What is BMI?
Let's take a step back, and go back in time to understand its meaning.
The concept of BMI has a history dating back to the year 1830 when it was intended to calculate normal weight for a population rather than an individual. Over the years, with the increase in BMI use, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) approved it in 1985, as a tool to assess obesity levels in populations and individuals. Consequently, organizations like WHO (World Health Organisation) further refined and standardized the BMI categories.
Currently, we measure BMI by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by their height in meters squared.
BMI = weight (kg) / [height (m)]2
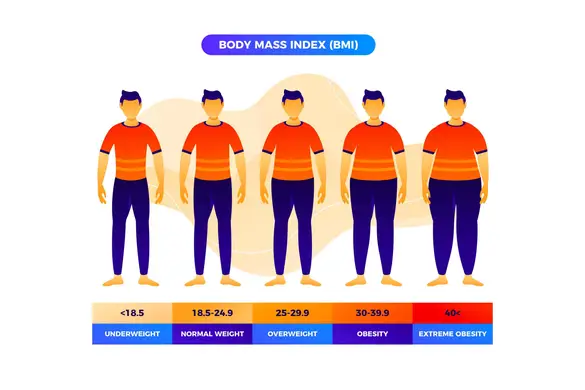
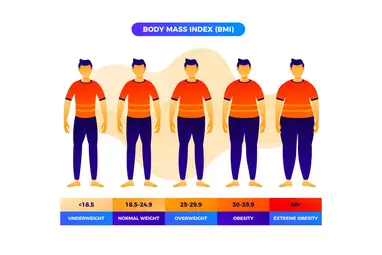
The result is categorized into the following BMI ranges indicating their weight status:
- BMI less than or equal to 18.5 indicates underweight
- BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 indicates an ideal and healthy weight
- BMI between 25 and 29.9 indicates an overweight
- BMI of 30 or higher indicates obesity
Knowing your BMI can help identify potential weight-related health risks and conditions. However, BMI should be interpreted with other health indicators and evaluated by a healthcare professional.
The Importance of BMI
People with a BMI range of 18.5 to 24.9 are generally considered healthy. However, people with a BMI lower than 18.5 are considered underweight and it is linked with higher risks of osteoporosis, fertility issues, and other complications.
On the contrary, nearly 2.8 million deaths per year are linked to being overweight or obese (BMI more than 25). In fact, the higher your BMI, the higher the risk of various health conditions, such as:
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Type 2 diabetes
- Certain types of cancer (breast, colon, prostate)
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- High cholesterol levels
- Sleep apnea
- Arthritis
- Liver disease
On the other hand, low BMI may lead to malnutrition, a weak immune system, muscle wasting, nutritional deficiency, and other health issues.
Knowing the BMI is a quick and inexpensive way to assess weight status, track any weight changes, and make informed decisions to mitigate the potential health risks associated with it through lifestyle adjustments.
However, please note that BMI alone does not provide a comprehensive health assessment. It is imperative to consult Healthcare professionals who will utilize BMI alongside other diagnostic tests and assessments to evaluate the health status and associated risks comprehensively.
What is the healthy BMI range and how to maintain it?<
The healthy BMI range is 18.5 to 24.9, and maintaining it can benefit you in several ways, including:
- Reduced risk of heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers
- Improved physical and mental well-being
- Increased energy levels and stamina
- Better sleep quality
- Improved fertility and reproductive health
You can follow these simple tips to maintain a healthy BMI range:
- Practice exercise regularly, brisk walking, strength training, and cardio
- Eat a balanced and nutritious diet
- Drink plenty of water and stay hydrated
- Indulge in stress management techniques for mental wellness
- Consult with healthcare experts or certified nutritionists for personalized treatment
Is BMI accurate?
While BMI is a useful screening tool and used widely to evaluate health status, it has some limitations, such as:
- Athletes who have lean muscle mass and a normal person with fat mass, both fall into the same BMI category, leading to misunderstanding, as it does not differentiate between lean body mass (muscle) and fat mass.
- BMI does not consider body fat distribution, which is an important factor for assessing health risks.
- BMI is not meant for certain populations, such as children, teenagers, pregnant individuals, or the elderly.
Summing up
Now you know how to use BMI and evaluate your health status to stay up to date with potential health risks and take preventive measures to stay in a healthy BMI range.
While BMI is just one piece of the puzzle, it should be used with caution and in conjunction with other health indicators. And consulting with a healthcare expert at GetSupp for personalized guidance and recommendations based on an individual's unique circumstances.
FAQs
What is a normal BMI?
A normal BMI ranges between 18.5 and 24.9 and is considered an ideal weight category.
What exactly does BMI measure, and how accurate is it as a health indicator?
BMI measures a person's body fat based on their weight and height. It is a primary screening tool that indicates potential weight problems and health issues arising due to weight issues. The higher the BMI, the higher the chance of health risks. However, BMI is not a perfect measurement and does not tell if the excess weight is from muscles or fat, which can be misleading sometimes. Therefore, it is best to use the BMI calculator as a starting point to identify the health status followed by other health measurements to confirm body fatness.
What are the different BMI categories (underweight, normal weight, etc.) and what do they mean for my health?
BMI results fall into four major categories:
Below 18.5: Underweight, which indicates malnutrition, nutritional deficiencies, metabolism problems or other health issues.
Between 18.5 and 24.9: Ideal weight, indicating a healthy weight.
Between 25 and 29.9: Overweight, which indicates risks of developing health problems like hypertension, and diabetes.
30 or over: Obese, indicative of risk of serious health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and hypertension.
How can I calculate my BMI, and are there any online calculators available?
The simple formula for calculating BMI is dividing weight in kilograms by height in meters squared (kg/m²).
BMI = weight (kg) / [height (m)]2
You can use the BMI calculator on GetSupp and quickly determine your BMI and understand your weight category.
Should I be concerned if my BMI falls outside the "normal" range?
Yes, if your BMI falls outside the normal BMI range, it suggests either you are in the underweight category or the overweight category, both of which indicate increased health risks. For the overweight category, the chances of heart disease, diabetes, and other weight-related issues increase, while the underweight category may indicate malnourishment and other health issues. You must try changing your diet and consult with a healthcare provider to discuss your BMI and any necessary lifestyle changes.
What are some limitations of using BMI as a sole measure of health and body composition?
BMI is a good measurement when used as a first step to identify health issues or body composition. However, BMI has some limitations, since it only considers weight and height and does not account for body composition such as muscle mass, bone density, and fat distribution. For example, individuals with high muscle mass but low body fat may still have high BMI which may be misleading, because by the rule high BMI equals high health risks. Additionally, BMI is similar for everyone and does not account for variations across different ages, sexes, and ethnicities, which can lead to wrong assessments in some populations.
For athletes or people with a lot of muscle mass, could a high BMI be misleading?
Yes, for athletes or individuals with significant muscle mass, a high BMI can be misleading because BMI can not distinguish between muscle and fat. Those with high muscle mass may be categorized as overweight or obese despite having low body fat. This further signifies the importance of considering other factors, such as body fat percentage and overall fitness when assessing health.
If my BMI indicates a potential health risk, what steps should I take next?
If your BMI indicates a potential health risk, start by switching to a healthier lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and maintained sleeping habits. You can consult with GetSupp health experts and nutritionists for consultation over a healthy lifestyle. Begin by cutting down the calorie intake and focus on burning more calories if you are overweight or obese. While adding more calories to your diet if you are overweight through mass gainers and weight gainers. However no matter your BMI range, it is important to include fiber-rich foods like vegetables, whole grains, and fruits, for a balanced diet and indulge in regular workouts to help manage your weight effectively.
Is being "overweight" or "obese" according to BMI always linked to negative health outcomes?
Generally, higher BMI levels are associated with increased risks of negative health outcomes because of increased fat around the body leading to high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and inflammation. However, in a few cases, individuals with muscle mass also have a high BMI but that does not indicate the same health risks as those with high body fat.
Where can I find reliable information and support for maintaining a healthy weight and lifestyle?
At GetSupp, you can get guidance and support to help you achieve a healthy BMI. Our resources include herbal supplements, weight loss aids, and expert advice from nutritionists. Whether you're starting your fitness journey or looking to maintain a healthy lifestyle, our team of experts is here to support you. For more information, tips, and advice, visit our blog or contact us to explore our services and meet our health professionals.

Health articles from our experts

List of Top 10 Bodybuilding Supplements For Muscle Gains

List of 15 Best Gut-Friendly Foods

Top Six Indian Recipes for Weight Loss

A Comprehensive Guide On How To Gain Weight Quickly

Muscle-Building Routine and Supplements for Maximum Gains

A Guide with Simple Tips To Follow For Weight Loss

Top 10 Foods That Are High in Protein

5 Best Whey Protein Powders in India
Understanding BMI: The Key to Weight-Health Connection

